Every day, many types of workers are exposed to chemicals in the workplace. The following is a breakdown of commonly used chemicals, where they are used, and exposure limits set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), or other regulatory organizations.
When employers establish an employee monitoring program and keep accurate monitoring records, safety and compliance issues are eliminated.
Healthcare Facilities:
 Halogenated Anesthetics
Halogenated Anesthetics
Commonly Used Chemicals: halothane (Fluothane®), enflurane (Ethrane®), isoflurane (Forane®), desflurane (Suprane®), and sevoflurane (Ultane®)
Where they are used: Operating rooms, PACU, veterinary clinics
Exposure limit: NIOSH recommends that no worker be exposed at concentrations greater than 2 ppm over a sampling period of greater than one hour (1977).
Recommended product: H-10-3 Halogenated Anesthetic Vapor Monitor
Nitrous Oxide
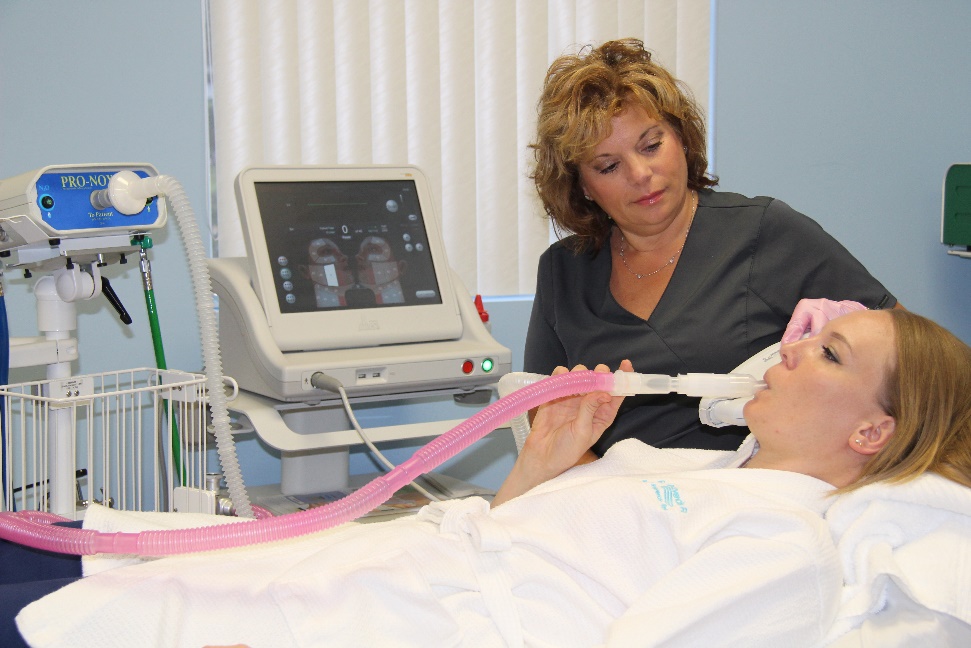 Where it is used: Operating rooms and dental clinics
Where it is used: Operating rooms and dental clinics
Exposure limit: The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) has set the Threshold Limit Value (TLV) at 50 ppm.
NIOSH has set a Recommended Exposure Limit (REL) of 25 ppm.
Recommended product: N-10 Nitrous Oxide Monitor
Formaldehyde
Where it is used: Laboratories, operating rooms, labor and delivery, morgues, and funeral homes
Exposure limits: Using a Time Weighted Average (TWA), an employee shouldn’t be exposed to airborne formaldehyde at levels greater than 0.75 ppm over an eight-hour period.
Using the Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL), an employee shouldn’t be exposed to airborne formaldehyde at levels greater than 2 ppm for greater than 15 minutes
Recommended product: F-50 Formaldehyde Vapor Monitor
Xylene
Where it is used: Histology labs
Exposure limit: OSHA recommends a TWA of no greater than 100 ppm over an eight-hour period.
Recommended product: OV-115 Xylene Vapor Monitor
Glutaraldehyde
 Where it is used: Gastroenterology departments, cardiology departments, endoscopy scope cleaning rooms, central supply, histology labs, and pathology labs
Where it is used: Gastroenterology departments, cardiology departments, endoscopy scope cleaning rooms, central supply, histology labs, and pathology labs
Exposure limits: NIOSH recommends an exposure limit of no greater than 0.2 ppm.
ACGIH recommends a threshold limit of 0.05 ppm.
Recommended product: G-10 Glutaraldehyde Vapor Monitor
Airborne Hydrogen Peroxide, Ortho-Phthalaldehyde (OPA), Peracetic Acid, or a Combination
Exposure limit: OSHA recommends a TWA of no greater than 1 ppm over an eight-hour period.
Recommended products: OP-10 O-Phthalaldehyde Vapor Monitor, OV-005 Acetic Acid Vapor Monitor, and HP-10 Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor Monitor
Ethylene Oxide
Where it is used: Central sterile processing area
Exposure limits: OSHA recommends a TWA of no greater than 1 ppm over an eight-hour period
NIOSH recommends a TWA of less than 0.1 ppm over an eight -hour period.
ACGIH recommends a TWA of no greater than 1 ppm over an eight-hour period.
ACGIH recommends a short-term exposure limit of 5 ppm for no longer than 15 minutes.
Recommended product: E-50 Ethylene Oxide Vapor Monitor
 Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Commonly used chemicals: Benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, xylene, styrene, acetone, MIK, and many other VOCs
VOCs can be found in new or renovated homes, manufactured homes, commercial buildings, RVs, and factories.
Recommended products: OV-00 Organic Vapor Monitor, OV-00F Full Scan Organic Vapor Monitor, OV-00IF Full Scan Organic Vapor Monitor for Indoor Air Quality, OV-095 BTEX + Saturated Hydrocarbon Vapor Monitor, and F-50I Formaldehyde Vapor Monitor for Indoor Air Quality
